第二講 : モデル
あなたは、今日の講義を聴くと、
モデル(考察対象システムの表現形)やモデリング(モデルを得ること)の重要さに気付き、
表現されたモデル(常微分方程式で表現されるもの)の代表的な表現方法を理解することができ、表現方法間の変換もできるようになります。
(講義内容一覧)
制御システムの設計手順
◆モデリング
◆モデルの分類 : 講義で扱う対象システムは主に線形常微分方程式系
◆モデル表現法(伝達関数、ブロック線図、状態方程式)
Systems
thinking is a discipline for
seeing wholes. It is a framework for seeing interrelationships rather
than
things, for seeing patterns of change rather than static “snapshots.”
It is a
set of general principles ― distilled over the course of the twentieth
century,
spanning fields as diverse as the physical and social sciences,
engineering,
and management.... During the last thirty years, these tools have been
applied
to understand a wide range of corporate, urban, regional, economic,
political,
ecological, and even psychological systems. And systems thinking is a
sensibility ― for the subtle interconnectedness that gives living
systems their
unique character.
Peter Senge

(前
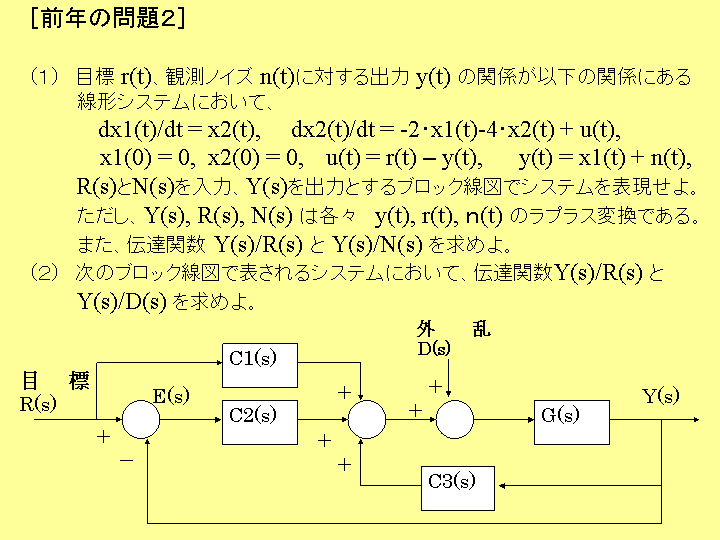
年の問題2の解答例)
(2) ブ
ロック線図より、
Y(s)
=
G(s) ・[ D(s) + U(s) ], U(s) = C1(s) ・R(s)
+ C2(s) ・E(s) + C3(s) ・Y(s), E(s) = R(s) – Y(s),
の各式を
得、これらから U(s)、E(s) を消去して一つの式に纏めると以下を得る。
[ 1
+
G(s)・C2(s) - G(s)・C3(s)]・Y(s)= G(s)・[ C1(s) + C2(s)]・R(s) + G(s)・D(s),
よって、伝
達関数は次となる。 Y(s)/R(s) = G(s)・[ C1(s) + C2(s)]/
[ 1 + G(s)・C2(s) - G(s)・C3(s)],
Y(s)/D(s) =
G(s)/ [ 1 + G(s)・C2(s) - G(s)・C3(s)],