
第三講 : 古典制御:システム解析1
あなた
は、今日の講義を理解すると、
なぜ状微分方程式を解くのにラプラス変換が使われるのかの理由が分かります。
(講義内容一覧)
◆ラプラス変換(Laplace
transformation)
◆伝達関数の定義と意味
◆ラプラス変換利用の線形常微分方程式の解法(線形常微分方程式を解くためのツールで
あるラプラス変換)
You
cannot teach a person anything; you can only help him find
it within
himself.
Galileo
Education
is the most powerful
weapon which you can use to change the world. Nelson Mandela
The
mediocre teacher tells, the good
teacher explains,
the
superior teacher demonstrates,
the great teacher inspires.
William
Arthur Ward
Bodily
exercise, when compulsory,
does no harm to the body;
but
knowledge which is acquired
under compulsion obtains no hold on the mind. Plato
演習問題3および(前
年の演習問題3とその解答例)

(前年の問
題3の解答)
(1) 伝達関数 G(s)
の定義は、出力信号のラプラス変換を入力信号のラプラス変換で割ったものである。意味としては、入力信号に対する出力信号の動的な応答特性を表すものであ
る。あるいは、単位インパルス入力に対する出力信号をラプラス変換したものである。
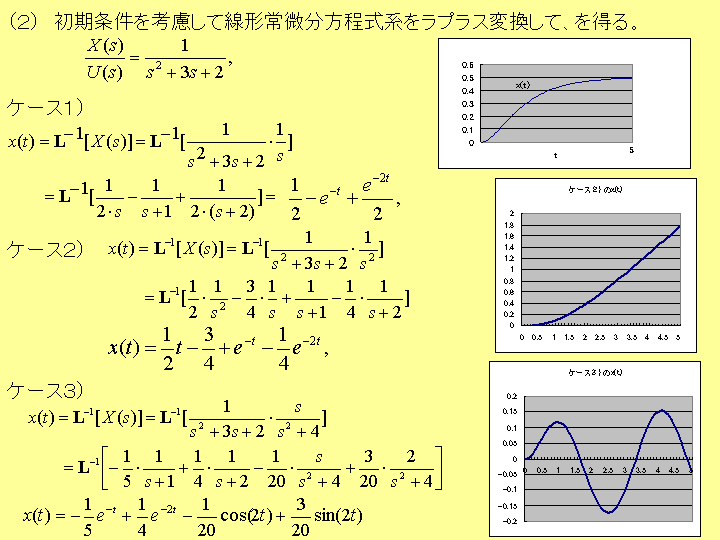
[問題3] (解答提出日は、第四講の日)
目標
r(t)、外乱 d(t)に対する出力
y(t) の関係が以下の関係にある線形システムにおいて、
dx1(t)/dt
=
- x1(t) + x2(t) + d(t),
dx2(t)/dt
= x1(t) -
2・x2(t)
+ u(t), x1(0) = 0, x2(0) = 0,
u(t)
= r(t) –
y(t), y(t) = x1(t),
(1) R(s)とD(s)を入力、Y(s)を出力とす
るブロック線図でシステムを表現せよ。
ただし、Y(s),
R(s), D(s) は各々y(t),
r(t), d(t) のラプラス変換である。
(2) 伝達関数 Y(s)/R(s)
と Y(s)/D(s) を求めよ。
(3) 以下のとき、このシステムの出力 y(t) を求め、概略図を描け。
d(t)=0 for
∀t, r(t)=2
for t≧ 0, r(t)=0 for t< 0